エージェントは、タスクを完遂するためにループ内でツールを使用する、大規模言語モデル (LLM) です。ToolLoopAgent クラスは、LLM・ツール・ループの 3 つのコンポーネントを処理します。
Vercel AI SDK 6.x : エージェント – 概要 / エージェントの構築
作成 : Masashi Okumura (@classcat.com)
作成日時 : 01/15/2026
バージョン : ai@6.0.35
* 本記事は ai-sdk.dev/docs の以下のページを参考にし、独自翻訳した上でまとめ直しています :
* サンプルコードの動作確認はしておりますが、必要な場合には適宜、追加改変しています。
* ご自由にリンクを張って頂いてかまいませんが、sales-info@classcat.com までご一報いただけると嬉しいです。
◆ お問合せ : 下記までお願いします。
- クラスキャット セールス・インフォメーション
- sales-info@classcat.com
- ClassCatJP
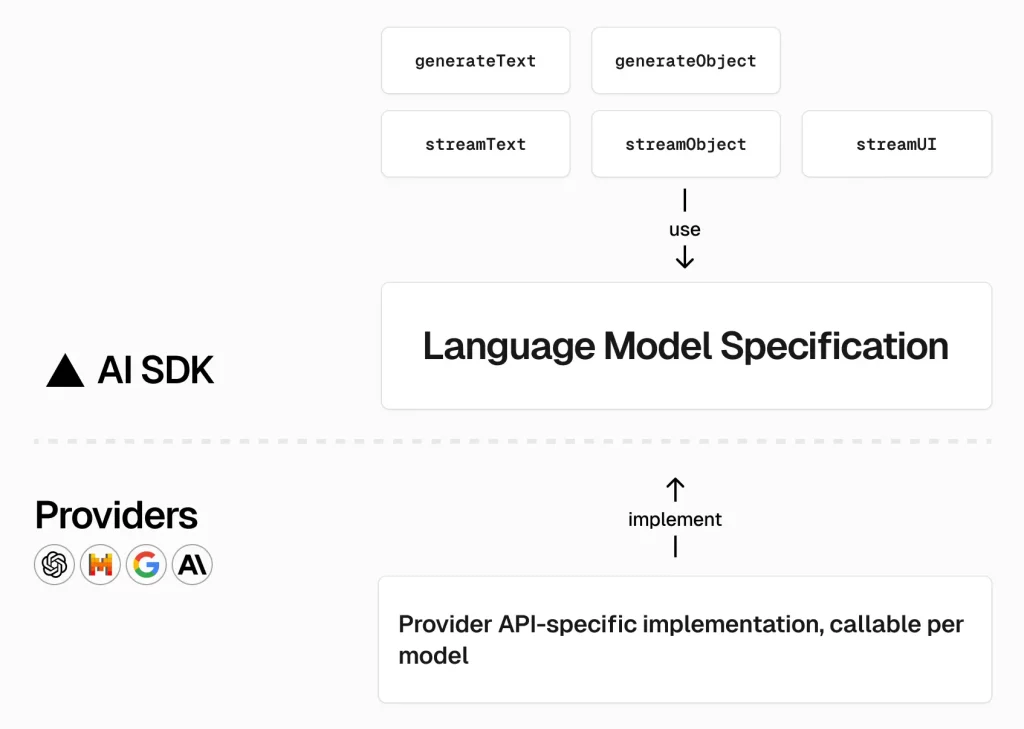
Vercel AI SDK 6.x : エージェント – 概要
エージェントは、タスクを完遂するためにループ内でツールを使用する、大規模言語モデル (LLM) です。
これらのコンポーネントは連携します :
- LLM は入力を処理して次のアクションを決定します
- ツール はテキスト生成 (ファイルの読み取り、API 呼び出し、データベースへの書き込み) を超えて機能を拡張します。
- ループ は以下を通して実行をオーケストレーションします :
- コンテキスト管理 – 会話履歴を維持し、各ステップでモデルが認識するもの (入力) を決定します。
- 停止条件 – ループ (タスク) がいつ完了するか決定します
- コンテキスト管理 – 会話履歴を維持し、各ステップでモデルが認識するもの (入力) を決定します。
ToolLoopAgent クラス
ToolLoopAgent クラスはこれら 3 つのコンポーネントを処理します。以下は、タスクを完遂するためにループ内で複数のツールを使用するエージェントです :
Gateway
import { ToolLoopAgent, stepCountIs, tool } from 'ai';
import { z } from 'zod';
const weatherAgent = new ToolLoopAgent({
model: "openai/gpt-4o-mini",
tools: {
weather: tool({
description: 'Get the weather in a location (in Fahrenheit)',
inputSchema: z.object({
location: z.string().describe('The location to get the weather for'),
}),
execute: async ({ location }) => ({
location,
temperature: 72 + Math.floor(Math.random() * 21) - 10,
}),
}),
convertFahrenheitToCelsius: tool({
description: 'Convert temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius',
inputSchema: z.object({
temperature: z.number().describe('Temperature in Fahrenheit'),
}),
execute: async ({ temperature }) => {
const celsius = Math.round((temperature - 32) * (5 / 9));
return { celsius };
},
}),
},
// Agent's default behavior is to stop after a maximum of 20 steps
// stopWhen: stepCountIs(20),
});
const result = await weatherAgent.generate({
prompt: 'What is the weather in San Francisco in celsius?',
});
console.log(result.text); // agent's final answer
console.log(result.steps); // steps taken by the agent
出力例
横浜の天気は摂氏で約25度です。
[
DefaultStepResult {
content: [ [Object], [Object] ],
finishReason: 'tool-calls',
rawFinishReason: undefined,
usage: {
inputTokens: 92,
inputTokenDetails: [Object],
outputTokens: 15,
outputTokenDetails: [Object],
totalTokens: 107,
raw: [Object],
reasoningTokens: 0,
cachedInputTokens: 0
},
warnings: [],
request: { body: [Object] },
response: {
id: 'aitxt-DvAAKbYGRcl5aPsJ2cR0HVCC',
timestamp: 2026-01-08T12:31:47.013Z,
modelId: 'openai/gpt-4o-mini',
headers: [Object],
body: [Object],
messages: [Array]
},
providerMetadata: { openai: [Object], gateway: [Object] }
},
DefaultStepResult {
content: [ [Object], [Object] ],
finishReason: 'tool-calls',
rawFinishReason: undefined,
usage: {
inputTokens: 121,
inputTokenDetails: [Object],
outputTokens: 19,
outputTokenDetails: [Object],
totalTokens: 140,
raw: [Object],
reasoningTokens: 0,
cachedInputTokens: 0
},
warnings: [],
request: { body: [Object] },
response: {
id: 'aitxt-i6odpheZW1LlDzPWlglfiE5b',
timestamp: 2026-01-08T12:31:48.026Z,
modelId: 'openai/gpt-4o-mini',
headers: [Object],
body: [Object],
messages: [Array]
},
providerMetadata: { openai: [Object], gateway: [Object] }
},
DefaultStepResult {
content: [ [Object] ],
finishReason: 'stop',
rawFinishReason: undefined,
usage: {
inputTokens: 155,
inputTokenDetails: [Object],
outputTokens: 17,
outputTokenDetails: [Object],
totalTokens: 172,
raw: [Object],
reasoningTokens: 0,
cachedInputTokens: 0
},
warnings: [],
request: { body: [Object] },
response: {
id: 'aitxt-BYjBIgIcUXGXtWpBXSyeYibz',
timestamp: 2026-01-08T12:31:48.842Z,
modelId: 'openai/gpt-4o-mini',
headers: [Object],
body: [Object],
messages: [Array]
},
providerMetadata: { openai: [Object], gateway: [Object] }
}
]
Provider
import { ToolLoopAgent, stepCountIs, tool } from 'ai';
import { openai } from "@ai-sdk/openai";
import { z } from 'zod';
const weatherAgent = new ToolLoopAgent({
model: openai("gpt-4o-mini"),
tools: {
weather: tool({
description: 'Get the weather in a location (in Fahrenheit)',
inputSchema: z.object({
location: z.string().describe('The location to get the weather for'),
}),
execute: async ({ location }) => ({
location,
temperature: 72 + Math.floor(Math.random() * 21) - 10,
}),
}),
convertFahrenheitToCelsius: tool({
description: 'Convert temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius',
inputSchema: z.object({
temperature: z.number().describe('Temperature in Fahrenheit'),
}),
execute: async ({ temperature }) => {
const celsius = Math.round((temperature - 32) * (5 / 9));
return { celsius };
},
}),
},
// Agent's default behavior is to stop after a maximum of 20 steps
// stopWhen: stepCountIs(20),
});
const result = await weatherAgent.generate({
prompt: 'What is the weather in San Francisco in celsius?',
});
console.log(result.text); // agent's final answer
console.log(result.steps); // steps taken by the agent
エージェントは自動的に以下を実行します :
- weather ツールを呼び出して華氏気温を取得します。
- convertFahrenheitToCelsius を呼び出してそれを変換します。
- 結果を含む最終的なテキストレスポンスを生成します。
Agent クラスは、ループ、コンテキスト管理、停止条件を処理します。
Agent クラスを使用する理由
Agent クラスは AI SDK でエージェントを構築する際に推奨されるアプローチです、何故ならばそれは :
- ボイラープレートの削減 – ループとメッセージ配列の管理
- 再利用性の向上 – 一度定義すれば、アプリケーションを通じて使用可能
- 保守性の単純化 – エージェント設定の更新を一元管理
殆どのユースケースでは、Agent クラスから始めてください。複雑な構造化ワークフローの各ステップに対する明示的な制御を必要とする場合、コア関数 (generateText, streamText) を使用してください。
構造化ワークフロー
エージェントは柔軟で強力ですが、非決定論的です。明示的な制御フローで信頼性のある反復可能な結果を必要とする場合、以下を組み合わせた構造化ワークフローパターンとともにコア関数を使用します :
- 明示的な分岐のための条件文
- 再利用可能なロジックのための標準関数
- 堅牢性のためのエラー処理
- 予測可能性のための明示的な制御フロー
Vercel AI SDK 6.x : エージェント – エージェントの構築
Agent クラスは LLM 設定、ツール、動作を再利用可能なコンポーネントにカプセル化する構造化手法を提供します。それはエージェントループを処理し、LLM が複雑なタスクを完遂するためにツールを連続的に複数回呼び出すことを可能にします。エージェントを一度定義すればアプリケーションにわたりそれらを使用できます。
ToolLoopAgent クラスを使用する理由
AI アプリケーションを構築する際、多くの場合以下が必要です :
- 設定の再利用 – アプリケーションの様々な部分にわたり同じモデル設定、ツール、プロンプトを利用
- 一貫性の維持 – コードベース全体で同じ動作と機能を保証する
- API ルートの単純化 – エンドポイントにおけるボイラープレートの削減
- 型安全 – エージェントのツールと出力に対して完全な TypeScript のサポートを得る
ToolLoopAgent クラスはエージェントの動作を定義するための単一の場所を提供します。
エージェントの作成
希望の設定で ToolLoopAgent クラスをインスタンス化してエージェントを定義します :
Gateway
import { ToolLoopAgent } from 'ai';
const myAgent = new ToolLoopAgent({
model: "openai/gpt-4o-mini",
instructions: 'You are a helpful assistant.',
tools: {
// Your tools here
},
});
構成設定オプション
Agent クラスは generateText と streamText と同じ設定すべてを受け取ります。以下を設定できます :
モデルとシステム指示
Gateway
import { ToolLoopAgent } from 'ai';
const agent = new ToolLoopAgent({
model: "openai/gpt-4o-mini",
instructions: 'You are an expert software engineer.',
});
ツール
エージェントがタスクを完遂するために使用できるツールを提供します :
Gateway
import { ToolLoopAgent, tool } from 'ai';
import { z } from 'zod';
const codeAgent = new ToolLoopAgent({
model: "openai/gpt-4o-mini",
tools: {
runCode: tool({
description: 'Execute Python code',
inputSchema: z.object({
code: z.string(),
}),
execute: async ({ code }) => {
// Execute code and return result
return { output: 'Code executed successfully' };
},
}),
},
});
ループ制御
デフォルトでは、エージェントは 20 ステップ (stopWhen: stepCountIs(20)) 実行されます。各ステップでモデルはテキストを生成するか、ツールを呼び出します。テキストを生成する場合、エージェントは完了します。ツールを呼び出す場合、AI SDK はそのツールを実行します。
エージェントが複数のツールを順番に呼び出すようにするには、stopWhen をより多くのステップを可能にするように設定します。各ツールの実行後、エージェントは新しい生成をトリガーし、そこではモデルは別のツールを呼び出したりテキストを生成できます :
Gateway
import { ToolLoopAgent, stepCountIs } from 'ai';
const agent = new ToolLoopAgent({
model: "openai/gpt-4o-mini",
stopWhen: stepCountIs(20), // Allow up to 20 steps
});
各ステップは一つの生成 (これはテキストかツール呼び出しのいずれかの結果になります) を表します。ループは以下の条件まで継続されます :
- ツール呼び出し以外の終了理由が返される、or
- 呼び出されたツールが実行関数を持たない、or
- ツール呼び出しが承認を必要とする、or
- 停止条件が満たされる
複数の条件を組み合わせることができます :
Gateway
import { ToolLoopAgent, stepCountIs } from 'ai';
const agent = new ToolLoopAgent({
model: "openai/gpt-4o-mini",
stopWhen: [
stepCountIs(20), // Maximum 20 steps
yourCustomCondition(), // Custom logic for when to stop
],
});
Learn more about loop control and stop conditions.
ツールの選択
エージェントがツールを使用する方法を制御します :
Gateway
import { ToolLoopAgent } from 'ai';
const agent = new ToolLoopAgent({
model: "openai/gpt-4o-mini",
tools: {
// your tools here
},
toolChoice: 'required', // Force tool use
// or toolChoice: 'none' to disable tools
// or toolChoice: 'auto' (default) to let the model decide
});
特定のツールの使用を強制することもできます :
Gateway
import { ToolLoopAgent } from 'ai';
const agent = new ToolLoopAgent({
model: "openai/gpt-4o-mini",
tools: {
weather: weatherTool,
cityAttractions: attractionsTool,
},
toolChoice: {
type: 'tool',
toolName: 'weather', // Force the weather tool to be used
},
});
構造化出力
構造化出力スキーマを定義します :
Gateway
import { ToolLoopAgent, Output, stepCountIs } from 'ai';
import { z } from 'zod';
const analysisAgent = new ToolLoopAgent({
model: "openai/gpt-4o-mini",
output: Output.object({
schema: z.object({
sentiment: z.enum(['positive', 'neutral', 'negative']),
summary: z.string(),
keyPoints: z.array(z.string()),
}),
}),
stopWhen: stepCountIs(10),
});
const { output } = await analysisAgent.generate({
prompt: 'Analyze customer feedback from the last quarter',
});
システム指示でエージェントの動作を定義
システム指示はエージェントの動作、パーソナリティと制約を定義します。それらはすべてのインタラクションのコンテキストを設定し、エージェントがユーザの質問にどのように応答し、ツールをどのように使用するかをガイドします。
基本的なシステム指示
エージェントのロールと専門知識を設定します :
Gateway
const agent = new ToolLoopAgent({
model: "openai/gpt-4o-mini",
instructions:
'You are an expert data analyst. You provide clear insights from complex data.',
});
エージェントの動作の制約
境界を設定して一貫した動作を確実にします :
Gateway
const customerSupportAgent = new ToolLoopAgent({
model: "openai/gpt-4o-mini",
instructions: `You are a customer support specialist for an e-commerce platform.
Rules:
- Never make promises about refunds without checking the policy
- Always be empathetic and professional
- If you don't know something, say so and offer to escalate
- Keep responses concise and actionable
- Never share internal company information`,
tools: {
checkOrderStatus,
lookupPolicy,
createTicket,
},
});
ツールの使用の指示
エージェントが利用可能なツールをどのように使用すべきかをガイドします :
Gateway
const researchAgent = new ToolLoopAgent({
model: "openai/gpt-4o-mini",
instructions: `You are a research assistant with access to search and document tools.
When researching:
1. Always start with a broad search to understand the topic
2. Use document analysis for detailed information
3. Cross-reference multiple sources before drawing conclusions
4. Cite your sources when presenting information
5. If information conflicts, present both viewpoints`,
tools: {
webSearch,
analyzeDocument,
extractQuotes,
},
});
フォーマットとスタイルの指示
出力フォーマットとコミュニケーション・スタイルを制御します :
Gateway
const technicalWriterAgent = new ToolLoopAgent({
model: "openai/gpt-4o-mini",
instructions: `You are a technical documentation writer.
Writing style:
- Use clear, simple language
- Avoid jargon unless necessary
- Structure information with headers and bullet points
- Include code examples where relevant
- Write in second person ("you" instead of "the user")
Always format responses in Markdown.`,
});
エージェントの使用
一度定義されれば、エージェントを 3 つの方法で使用できます :
テキスト生成
const result = await myAgent.generate({
prompt: 'What is the weather like?',
});
console.log(result.text);
テキストのストリーミング
ストリーミング応答のために stream() を使用します :
const stream = myAgent.stream({
prompt: 'Tell me a story',
});
for await (const chunk of stream.textStream) {
console.log(chunk);
}
UI メッセージへの応答
createAgentUIStreamResponse() を使用してクライアント・アプリケーションへの API レスポンスを作成します :
// In your API route (e.g., app/api/chat/route.ts)
import { createAgentUIStreamResponse } from 'ai';
export async function POST(request: Request) {
const { messages } = await request.json();
return createAgentUIStreamResponse({
agent: myAgent,
messages,
});
}
End-to-end な型安全性
エージェントの UIMessage の型を推論できます :
import { ToolLoopAgent, InferAgentUIMessage } from 'ai';
const myAgent = new ToolLoopAgent({
// ... configuration
});
// Infer the UIMessage type for UI components or persistence
export type MyAgentUIMessage = InferAgentUIMessage;
useChat を使用してクライアント・コンポーネントでこの型を使用します :
components/chat.tsx
'use client';
import { useChat } from '@ai-sdk/react';
import type { MyAgentUIMessage } from '@/agent/my-agent';
export function Chat() {
const { messages } = useChat();
// Full type safety for your messages and tools
}
以上
