LangGraph は会話エージェントの構築のために不可欠な 2 種類のメモリ (短期メモリ & 長期メモリ) をサポートしています。このガイドは LangGraph のエージェントで両方のメモリタイプを使用する方法を示します。
LangGraph : Prebuilt エージェント : メモリ
作成 : クラスキャット・セールスインフォメーション
作成日時 : 06/15/2025
* 本記事は langchain-ai.github.io の以下のページを独自に翻訳した上で、補足説明を加えてまとめ直しています :
* サンプルコードの動作確認はしておりますが、必要な場合には適宜、追加改変しています。
* ご自由にリンクを張って頂いてかまいませんが、sales-info@classcat.com までご一報いただけると嬉しいです。
◆ お問合せ : 下記までお願いします。
- クラスキャット セールス・インフォメーション
- sales-info@classcat.com
- ClassCatJP
LangGraph : Get started : Prebuilt エージェント : メモリ
LangGraph は会話エージェントの構築のために不可欠な 2 種類のメモリをサポートしています :
このガイドは LangGraph のエージェントで両方のメモリタイプを使用する方法を示します。メモリの概念の深い理解のためには、LangGraph メモリ・ドキュメント を参照してください。
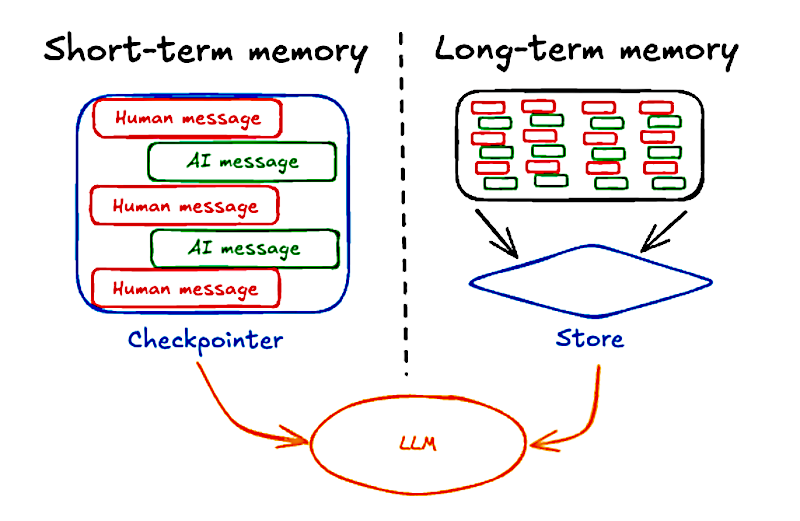
短期メモリ も 長期メモリ も両方とも LLM インタラクション全体に渡り連続性を維持するには永続的なストレージを必要とします。プロダクション環境では、このデータは通常はデータベースに保存されます。
Terminology : LangGraph では :
- 短期メモリはまた スレッドレベル (thread-level) メモリ とも呼ばれます。
- 長期メモリはまた クロススレッド (cross-threa) メモリ とも呼ばれます。
スレッド は、同じ thread_id でグループ化された一連の関連する実行を表します。
短期メモリ
短期メモリはエージェントが複数ターンの会話を追跡することを可能にします。それを使用するには、以下が必要です :
- エージェントを作成するときチェックポインターを提供します。チェックポインターはエージェント状態を 永続化 できます。
- エージェントを実行するとき、config で thread_id を供給します。thread_id は会話セッションのための一意の識別子です。
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import InMemorySaver
checkpointer = InMemorySaver()
def get_weather(city: str) -> str:
"""Get weather for a given city."""
return f"It's always sunny in {city}!"
agent = create_react_agent(
model="anthropic:claude-3-7-sonnet-latest",
tools=[get_weather],
checkpointer=checkpointer
)
# Run the agent
config = {
"configurable": {
"thread_id": "1"
}
}
sf_response = agent.invoke(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "what is the weather in sf"}]},
config
)
# Continue the conversation using the same thread_id
ny_response = agent.invoke(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "what about new york?"}]},
config
)
エージェントが同じ thread_id で 2 度目に呼び出される場合、最初の会話の元のメッセージ履歴は自動的に含まれ、エージェントはユーザがニューヨークの天気について具体的に尋ねていることを推論できます。
Note : LangGraph Platform は production-ready なチェックポインターを提供します。
LangGraph Platform を使用している場合、配備中、チェックポインターは production-ready データベースを使用するように自動的に設定されます。
メッセージ履歴の管理
長い会話は LLM のコンテキスト・ウィンドウを超える可能性があります。一般的な解決法は :
これはエージェントが、LLM のコンテキスト・ウィンドウを超えることなく、会話を追跡することを可能にします。
メッセージ履歴を管理するには、pre_model_hook を指定します – これは言語モデルを呼び出す前に常に実行される関数 ( ノード ) です。
メッセージ履歴を要約する
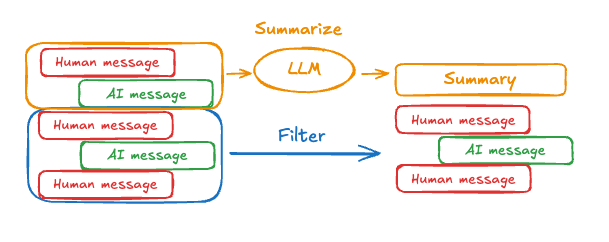
メッセージ履歴を要約するには、事前構築済みの SummarizationNode で pre_model_hook を使用できます :
from langchain_anthropic import ChatAnthropic
from langmem.short_term import SummarizationNode
from langchain_core.messages.utils import count_tokens_approximately
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
from langgraph.prebuilt.chat_agent_executor import AgentState
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import InMemorySaver
from typing import Any
model = ChatAnthropic(model="claude-3-7-sonnet-latest")
summarization_node = SummarizationNode(
token_counter=count_tokens_approximately,
model=model,
max_tokens=384,
max_summary_tokens=128,
output_messages_key="llm_input_messages",
)
class State(AgentState):
# NOTE: we're adding this key to keep track of previous summary information
# to make sure we're not summarizing on every LLM call
context: dict[str, Any]
checkpointer = InMemorySaver()
agent = create_react_agent(
model=model,
tools=tools,
pre_model_hook=summarization_node,
state_schema=State,
checkpointer=checkpointer,
)
メッセージ履歴のトリミング
メッセージ履歴をトリムするには、trim_messages 関数で pre_model_hook を使用します :
from langchain_core.messages.utils import (
trim_messages,
count_tokens_approximately
)
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
# This function will be called every time before the node that calls LLM
def pre_model_hook(state):
trimmed_messages = trim_messages(
state["messages"],
strategy="last",
token_counter=count_tokens_approximately,
max_tokens=384,
start_on="human",
end_on=("human", "tool"),
)
return {"llm_input_messages": trimmed_messages}
checkpointer = InMemorySaver()
agent = create_react_agent(
model,
tools,
pre_model_hook=pre_model_hook,
checkpointer=checkpointer,
)
pre_model_hook を使用してメッセージ履歴を管理する方法についての詳細を学習するには、この how-to ガイド をご覧ください。
ツール内での読み取り
LangGraph はエージェントがツール内で短期メモリ (状態) にアクセスすることを可能にします。
from typing import Annotated
from langgraph.prebuilt import InjectedState, create_react_agent
class CustomState(AgentState):
user_id: str
def get_user_info(
state: Annotated[CustomState, InjectedState]
) -> str:
"""Look up user info."""
user_id = state["user_id"]
return "User is John Smith" if user_id == "user_123" else "Unknown user"
agent = create_react_agent(
model="anthropic:claude-3-7-sonnet-latest",
tools=[get_user_info],
state_schema=CustomState,
)
agent.invoke({
"messages": "look up user information",
"user_id": "user_123"
})
See the Context guide for more information.
ツールからの書き込み
実行中にエージェントの短期メモリ (状態) を変更するには、ツールから直接、状態更新を返すことができます。これは、中間結果を永続化したり、続くツールやプロンプトが情報にアクセスできるようにするために有用です。
from typing import Annotated
from langchain_core.tools import InjectedToolCallId
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableConfig
from langchain_core.messages import ToolMessage
from langgraph.prebuilt import InjectedState, create_react_agent
from langgraph.prebuilt.chat_agent_executor import AgentState
from langgraph.types import Command
class CustomState(AgentState):
user_name: str
def update_user_info(
tool_call_id: Annotated[str, InjectedToolCallId],
config: RunnableConfig
) -> Command:
"""Look up and update user info."""
user_id = config["configurable"].get("user_id")
name = "John Smith" if user_id == "user_123" else "Unknown user"
return Command(update={
"user_name": name,
# update the message history
"messages": [
ToolMessage(
"Successfully looked up user information",
tool_call_id=tool_call_id
)
]
})
def greet(
state: Annotated[CustomState, InjectedState]
) -> str:
"""Use this to greet the user once you found their info."""
user_name = state["user_name"]
return f"Hello {user_name}!"
agent = create_react_agent(
model="anthropic:claude-3-7-sonnet-latest",
tools=[update_user_info, greet],
state_schema=CustomState
)
agent.invoke(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "greet the user"}]},
config={"configurable": {"user_id": "user_123"}}
)
For more details, see how to update state from tools.
長期メモリ
長期メモリを使用して、ユーザ固有またはアプリケーション固有の会話全体に渡るデータをストアします。これは、ユーザの優先設置やその他の情報を記憶したい、チャットボットのようなアプリケーションに有用です。
長期メモリを使用するには、以下が必要です :
READ
A tool the agent can use to look up user information
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableConfig
from langgraph.config import get_store
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
from langgraph.store.memory import InMemoryStore
store = InMemoryStore()
store.put(
("users",),
"user_123",
{
"name": "John Smith",
"language": "English",
}
)
def get_user_info(config: RunnableConfig) -> str:
"""Look up user info."""
# Same as that provided to `create_react_agent`
store = get_store()
user_id = config["configurable"].get("user_id")
user_info = store.get(("users",), user_id)
return str(user_info.value) if user_info else "Unknown user"
agent = create_react_agent(
model="anthropic:claude-3-7-sonnet-latest",
tools=[get_user_info],
store=store
)
# Run the agent
agent.invoke(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "look up user information"}]},
config={"configurable": {"user_id": "user_123"}}
)
WRITE
Example of a tool that updates user information
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langgraph.config import get_store
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
from langgraph.store.memory import InMemoryStore
store = InMemoryStore()
class UserInfo(TypedDict):
name: str
def save_user_info(user_info: UserInfo, config: RunnableConfig) -> str:
"""Save user info."""
# Same as that provided to `create_react_agent`
store = get_store()
user_id = config["configurable"].get("user_id")
store.put(("users",), user_id, user_info)
return "Successfully saved user info."
agent = create_react_agent(
model="anthropic:claude-3-7-sonnet-latest",
tools=[save_user_info],
store=store
)
# Run the agent
agent.invoke(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "My name is John Smith"}]},
config={"configurable": {"user_id": "user_123"}}
)
# You can access the store directly to get the value
store.get(("users",), "user_123").value
セマンティック検索
LangGraph はまた、セマンティック類似性により長期メモリ内の項目を 検索する こともできます。
Prebuilt メモリツール
LangMem は、エージェントで長期メモリを管理するためのツールを提供する、LangChain-maintained ライブラリです。See the LangMem documentation for usage examples.
追加リソース
以上
